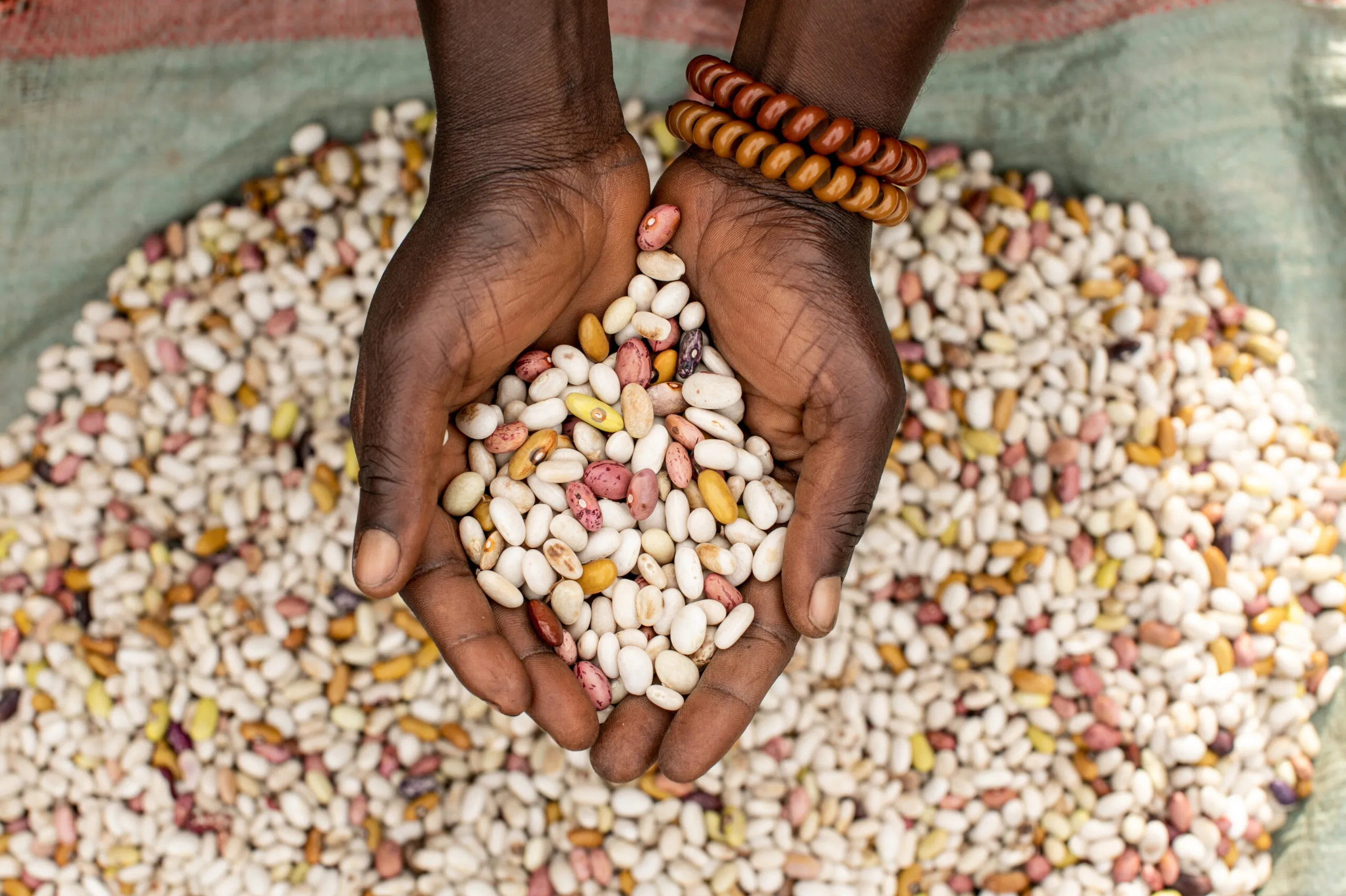
Growth is not enough (Technical Research – Download #1): This study examines how gender and economic inequality play a role in the global hunger crisis against socio-political, economic, and climate shocks. Very little empirical research focuses on national-level food security and its linkages with gender inequality, economic inequality, and significant macroeconomic factors like agricultural production and economic growth. This research explores these linkages and how the dynamics are changing during the pre- and post-pandemic periods.
Growth is not enough (Policy Paper – Download #2): This summarizes the findings from the technical report that economic growth is not enough to solve the global hunger crisis and draws from broader literature as to why and where this is happening. Through country case studies, it explores the challenges of the global hunger crisis and ways to solve it.
Growth is not enough (two-page summary – Download #3): This two-pager summarises the research above.